- Our College
- Academics
- Student Services
- Public Reports
- Forum
- Library
- Quick Access
AP Full Official:AAS ElectronicsTechnology
Campus: Pohnpei Campus
Completed by: Nelchor T. Permitez
AP Review Submission Date: March 2014
AR Review Cycle: 2012-2013
The Electronic Technology Program will provide much needed vocational and technical training to all the Nation’s States. Its primary purpose is to provide students with marketable entry-level skills in the electronic industry or any related field/career. The program qualifies students to take external licensure, vendor-based, or skill standards examinations in the field. If standardized external exams are not available in the field of study, the program prepares students at skill levels expected of employees in an occupation found in the workforce. The academic and technical coursework will also prepare students to pursue advanced training in the area at higher institution.
Its aim is to make student successful in the field of applied electronics science and technology and become competent in servicing and troubleshooting of electronic circuits and devices.
The program was created by recommendations of Pohnpei Campus Advisory Council to offer a certificate of achievement (COA) in electronics to train local students to acquire skills in maintaining and repairing of electronic equipment and devices which was a needed skill in the community and the local workforce.
Milestones:
Maintenance, troubleshooting, repairing and modifying electronics equipment and systems is the base for a career as a technician in this high-tech field. The computer and information technologies are driving the need for more maintenance and repair services. The academic course work, technical skills training and practical experience available in this program prepare the student for positions within the industry. Training on and with the state of the art computer aided instruction system at COM-FSM will provide the technical edge needed in today’s telecommunications industry. Embedded within the program are three separate exit points, Certificate of Achievement in Electronics Engineering Technology, Advance Certificate in Electronics Technology and the Associate of Applied Science in Electronics Technology. Figure 1, show the entry and exit points for electronics program.
The admission requirements for ET programs follow the same the admission requirements for all certificates of achievement programs as offered by the College in which students must complete high school education or equivalence to enter in either program.
Students must be admitted into degree programs based on the results of the College of Micronesia-FSM Entrance Exam (COMET) to further their studies into the Advanced Certificate and Associate of Applied Science degree. Students who are admitted into the programs as certificate bound status must change their status to degree bound by retaking and passing the COMET into the degree programs.
Certificate of Achievement in Electronic Engineering Technology
General Education Requirements................................................15credits
Mathematics (8)
MS 104 Technical Math I (4)
MS 106 Technical Math II (4)
Computer Applications (3 credits)
CA 100 Computer Literacy (3)
Natural Science (4 credits)
Any Science with lab: [preferably SC130 Physical Science]
Technical Requirements................................................22credits
VEE 103 Electronic Fundamentals I (3)
VSP 121 Industrial Safety (1.5)
VEE 100 Soldering and Mechanical Termination Techniques (1.5)
VEM 110 Workshop Fabrications (3)
VEE 104 Electronic Fundamentals II (4)
VEE 110 Discrete Devices I (3)
VEE 125 Electronic Circuits (3)
VEE 135 Digital Electronics I (3)
Total Requirements................................................37credits
Advanced Certificate in Telecommunication Technology
General Education Requirements ................................(3 credit)
EN 123 Technical Communications (3)
Technical Elective (2)
(Student may choose any technical course subject to approval by division)
VEE 250 Co-operative Education (2)
VTE 281 Cellular Phone Repairs (3)
Sub Total Requirements................................14 credits
Certificate of Achievement ................................37 credits
Total Requirements...................................51 credits
Advanced Certificate in Electronic Technology
General Education Requirements................................3 credits
EN 123 Technical Communications (3)
Technical Requirements................................ 12 credits
VEE 223 PC Hardware & Software (4)
VEE 222 Discrete Devices II (3)
VEE 235 Digital Electronic II (3)
Associate of Applied Science in Electronic Technology
General Education Requirements..........................4 credits
Humanities (3)
Any course in art, music, history, language, philosophy (3)
Physical Education (1)
Any Physical Education course
Technical Major Requirements............................11 credits
VEE 224 Video Systems & Product Servicing (4)
VEE 225 Business Machines & Servicing (4)
VEE 240 Signal Processing (3)
Sub Total Requirements............................ 15 credits
Advanced Certificate in Electronic Technology............................ 52 credits
Graduation Requirements................................ 67 credits
Source: COM-FSM General Catalog
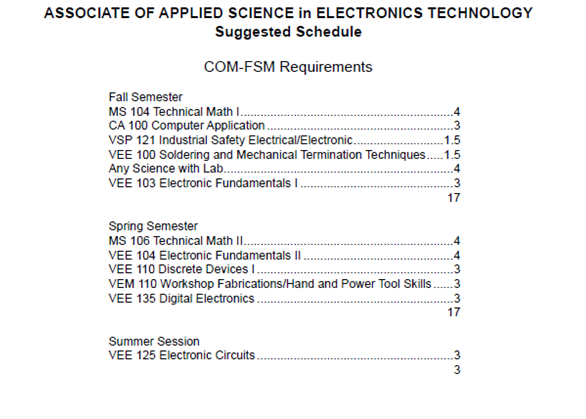

Source: COM-FSM General Catalog
| Course | Fall 12 | Spring 12 | Fall 13 | Spring 13 |
| VEE222 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| VEE222 | 13 | 16 | 10 | 10 |
| VEE224 | 13 | 13 | ||
| VEE225 | 14 | 13 | ||
| VEE230 | 8 | 12 | 12 | |
| VEE235 | 13 | 17 | ||
| VEE240 | 15 | 11 | 14 | |
| VEE250 | /td> | 13 |
Table 1. AAS ET program courses and enrollment.
The table 1, shows the courses for AAS ET and the number of students for each semester which form 1 section at Pohnpei campus for AY2012-2013. Source COM-FSM website IRPO data.
Full-time Faculty
Part Time Faculty
Note: Faculty to Student Ratio: 1:15
| Assessment of course student learning outcomes of program courses | See appendix 1, The result shows the technical courses offered in AAS ET for AY2012-2013. Each have Course Student learning Outcome, Assessment strategies and Target & task, result and Improvement & follow-up. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assessment of program student learning outcomes | See appendix 2, The result shows the AAS ET for AY2012-2013 Program Learning Outcome result divided into four column namely: Goal, Program student learning outcomes, Assessment strategies and Target & task, result and Improvement & follow-up. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Program enrollment (historical enrollment patterns, student credits by major) |
Table 2. AAS ET Program Enrollment The table 2, shows the number of students on AAS ET program for AY 2012-2013 fall and spring semester. Also the average credit enrolled for each semester including the number of credits. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average class size |
Table 3. AAS ET Program section, enrollment ratio and average class size. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Course completion rate |
Table 4. AAS EY Course Completion Rate.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Student persistence rate (semester to semester) |
Table 5. Student Persistence Data. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Student retention rate (Fall-to-Fall for two-year programs; Fall-to-Spring for one-year programs) |
Table 6. AAS ET Student Retention Data. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Success rates on licensing or certification exams (CTE, TP, Nursing, etc) | Currently there is no certification or licensing exams in place in FSM however the courses are currently in process aligning the competency skills requirements to pass on Electronics Technician Association (ETA) in United States to meet the current industry standards set forth by the association. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Graduation rate based on yearly number | Graduation head count at COM_FSM PNI campus
Table 7. Graduation head count at COM_FSM PNI campus. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Student Seat Cost |
Table 8. Student seat cost for AY 2012-2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of duplicate or redundant courses, programs or services | NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Students' satisfaction rate | The division of technology and trade come up with its own student satisfaction rating form that will measure the satisfaction of the student in the program courses as instructors methodology, program materials, equipment acquired knowledge and learned skills. Using the four point Likert scale, 25 student respondents who evaluated the course offered in AAS ET the total computed mean rate is 3.8 which means satisfactory rating. Source AY2012-2013 students evaluation form. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alumni data | From the 16 students graduate for AY2012-2013, 4 student pursue bachelors education in mainland and COM-FSM 12 are locally employed however not related to the program they finish which is consider as “underemployed”. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Employment data and employer feedback (employer survey) | High-tech service shop hired one of our student graduate and the head technician rate him satisfactory in the workplace for he knows how to follow instruction as assigned. However our graduate did not stay there for long for he find another job opportunity which is close to his house. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Program added or cancelled at nearby regional institutions (PCC, GCC, Hawaii schools, UOG, CMI, NMC) | The following regional schools offers same program on different nomenclature that of COM-FSM are as follows: PCC offers AAS General Electronics GCC handles Secondary CTE Program in electronics Hawaii Community College offers AAS in Electronics Technology Honolulu Community College offers Associate in Science (AS) Degree in the Computing, Electronics, and Networking Technology program The program offerings of the regional institution does not have significant impact on the student in-flow and out-flow base on the trending of registration for AY 2012-2013. The graduate student usually pursue further education on these institution for bachelors degree. The program meet the regular average number of students for each course for each semester in AY 2012-2013. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer rate | For AY 2012-2013, there is 1 recorded and track that pursue education to bachelors program at U.S. mainland and 3 to another AS degree program in COM-FSM. |
It is recommended the following strategy should be adopted to ensure the sustainability of AAS ET program and meet the industry demand for Electronics technician.
This website and all COM-FSM Internet based services are best viewed with Firefox 3.0 or better.
© Copyright 2020 College of Micronesia-FSM | Site Disclaimer
P. O. Box 159, Kolonia, Pohnpei, 96941 - (691) 320-2480
College of Micronesia-FSM is accredited by the Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges,
Western Association of Schools and Colleges, 428 J Street., Suite 400 Sacramento, CA 95814, (415) 506-0234,
an institutional accrediting body recognized by the Council for Higher Education Accreditation and the U.S. Department of Education.
Additional information about accreditation, including the filing of complaints against member institutions, can be found at: www.accjc.org