Thermal Linear Expansion Laboratory
Purposes
- To determine the coefficient of thermal linear expansion for three different materials.
Set Up
Due to the limited number of materials, we will be exploring these systems as a class.
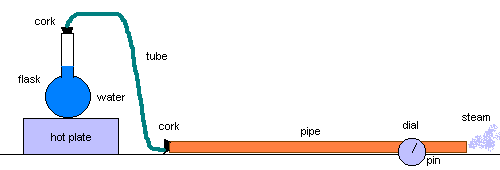
Measurements (include the units!)
| Description of object |
Var |
Copper pipe |
Steel pipe |
PVC pipe |
| The initial length of the pipe |
Li |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| The initial temperature of the pipe |
ti |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| The final temperature of the pipe |
tf |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| Calculated change in temperature |
tf - ti |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| The degrees of rotation of the dial |
q |
__________° |
__________° |
__________° |
| The diameter of the pin |
d |
0.00065 m |
0.00065 m |
0.00065 m |
| Calculated change in length |
DL |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| Calculated coeficient of linear expansion |
a |
__________ |
__________ |
__________ |
| Calculated error in a |
ea |
__________ |
__________ |
|
Procedure
- Take the initial measurements.
- Run steam through the pipe. Lay pipe on paper towels, swathe in paper towels to
prevent heat loss. Set three to four thermometers under the towels on the pipe to
monitor the pipe temperature. Recommend that only two of the three pipes above be used: it
can take up to an hour for the full pipe length to heat to around 70°C. Copper and
PVC worked well. Alternative: find a system that delivered more steam than the flask
system that was used Spring 2000.
- Observe the rotation of the dial
- Wait until the full length of the pipe is at the final temperature.
- Record the rotation in degrees of the dial.
Calculations
p = 3.141592
DL = (p × d)(q/360°)
The coeficient of linear expansion a can be determined from
the formula for linear expansion:
DL = a Li Dt
DL = a Li [tf
- ti]
a = DL/(Li[tf
- ti])
Use the following table to calculate your percentage error ea:
| material |
a/°C) |
material |
a/°C) |
| aluminum |
24 ×10-6 |
glass, pyrex |
3.6 ×10-6 |
| brass |
19 ×10-6 |
iron |
12 ×10-6 |
| concrete |
12 ×10-6 |
lead |
29 ×10-6 |
| copper |
17 ×10-6 |
quartz |
0.5 ×10-6 |
| glass, crown |
9 ×10-6 |
steel |
12 ×10-6 |
Homework
- Which material examined in the lab expands the most when heated?
- Which material examined in the lab expands the least when heated?
- What will the change in length be for a 5.0 meter PVC pipe in Minneapolis, Minnesota
between winter and summer if the winter temperature is -15°C and the summer temperature
is 30°C?
- From the perspective of linear expansivity, why cannot rebar used in concrete be made
from a light but strong and corrosion resistant material such as aluminum?
- Why is copper pipe preferred by plumbers for connecting sinks to the pipes in the wall?
SC 130 Home page
Lee Ling's Courses Home Page
 To COM-FSM Home Page
To COM-FSM Home Page


![]() To COM-FSM Home Page
To COM-FSM Home Page