- diarhea
- fever
- head colds
- menstrual cramping
- toothache
- That Clerodendrum inerme fever usage information cannot be published without careful protection of indigenous intellectual property rights.
- That Clerodendrum inerme is effective in reducing fevers.
- That Clerodendrum inerme is ethnobotanically irrelevant due to its widespread usage.
- That Clerodendrum inerme usage is probably a well kept secret not shared with outsiders.
- Bird's nest fern
- Black pepper
- Breadfruit
- Clove tree
- Coffee
- Cycad
- Nutmeg tree
- Pine tree

- __________
- __________
- __________

- __________
- __________
- __________
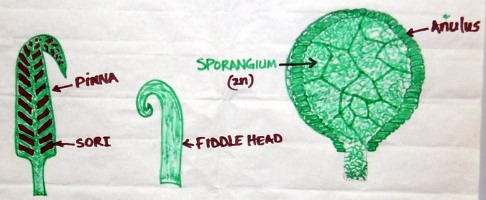
Explain the function and botanical importance of fern sori.