 CS 161 - Introduction to Programming with PHP
CS 161 - Introduction to Programming with PHP
Computer Organization
- Input unit
- Output unit
- Memory unit
- Arithmetic and logic unit
- Central processing unit
- Secondary storage unit
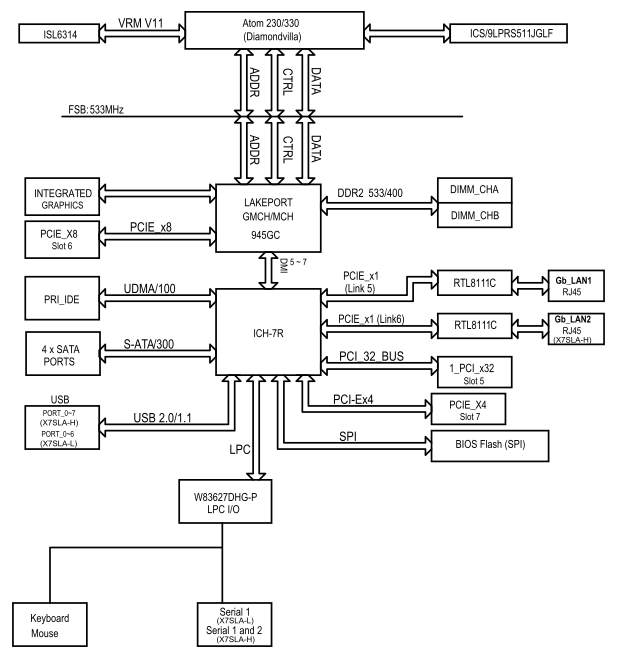
Sample block diagram from a Supermicro Atom system:
How computers store data, i.e. data types understood by the CPU:
- boolean
- integer
- float
Data types that are understood by PHP:
- Scalar:
- boolean
- integer
- float
- string
- Compound:
- array
- object
- Special:
- resource
- NULL
From the PHP documentation:
The type of a variable is usually not set by the programmer; rather, it is decided at runtime by PHP depending on the context in which that variable is used.
Operators (see Chapter 15. Operators)
- Arithmetic
- String
- Comparison
- Assignment
Assignment #2 Due: Friday 24 September
Problem #1:
The following PHP code:
<?php printf("%d\n", 55); printf("%d\n", 055); printf("%d\n", "055"); ?>Produces the following ouput:
55 45 55Question: Why? (clue: what does 0x55 print as?)
Problem #2:
Write a program that determines the number of pennies, nickels, dimes, quarters, and dollar bills that are needed to make correct change for a user-entered amount of purchase and payment.
The following code can be used to request input from the user:
$line = trim(fgets(STDIN)); // reads one line from STDIN
Goals of assignment: learn about PHP data types